Foods to lower cholesterol are essential for anyone looking to improve their heart health and overall well-being. With cholesterol levels linked to various health issues, understanding how dietary choices can make a significant difference is crucial. From the types of cholesterol to the impact of certain foods on cholesterol levels, this discussion will guide you through the intricate relationship between what you eat and how it affects your health.
Managing cholesterol is not just about avoiding bad foods; it’s about embracing a variety of cholesterol-lowering options that can boost your health. By incorporating specific foods into your daily diet, you can take proactive steps toward maintaining balanced cholesterol levels and improving your lifestyle.
Introduction to Cholesterol

Source: draxe.com
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood that plays a vital role in building healthy cells. While your body needs cholesterol to produce hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods, having high levels of certain types of cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease. Understanding the types of cholesterol and managing their levels is crucial for maintaining overall health.There are two main types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, as high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, which may result in heart attacks and strokes. On the other hand, HDL is known as “good” cholesterol, as it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream. Striking a balance between these two types is essential for cardiovascular health.
Diet and Its Impact on Cholesterol Levels
The connection between diet and cholesterol levels is significant and cannot be overlooked. Certain foods can help lower LDL levels while raising HDL levels, making dietary choices critical for managing cholesterol effectively. Here are some dietary changes that can positively influence cholesterol levels:
Incorporating healthier fats
Opt for unsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts instead of saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy products. These healthier fats can help improve your cholesterol profile.
Fiber-rich foods
Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, lentils, and fruits, can help lower LDL cholesterol by binding to it in the digestive system and removing it from the body.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can improve heart health and help raise HDL cholesterol levels.
Plant sterols and stanols
These natural substances found in plants can block the absorption of cholesterol and are available in fortified foods and supplements.
Limit processed and sugary foods
Reducing the intake of foods high in trans fats and added sugars can significantly improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.By being mindful of dietary choices, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their cholesterol levels, which is instrumental in reducing the risk of heart-related issues.
Understanding Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol levels are a key indicator of heart health, influencing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Understanding what constitutes normal, borderline, and high cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining overall wellness and making informed health decisions. Cholesterol is primarily categorized into two types: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). The balance between these two types of cholesterol plays a significant role in determining overall health.
Here’s a breakdown of normal cholesterol level ranges and their implications:
Normal Cholesterol Level Ranges
The following ranges indicate the levels of total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL, along with their significance:
| Cholesterol Type | Desirable Level | Borderline High Level | High Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol | Less than 200 mg/dL | 200-239 mg/dL | 240 mg/dL and above |
| LDL Cholesterol | Less than 100 mg/dL | 100-129 mg/dL | 130 mg/dL and above |
| HDL Cholesterol | 60 mg/dL and above | 40-59 mg/dL | Less than 40 mg/dL |
Maintaining a total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dL is generally regarded as heart-healthy. Higher levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease. Balanced LDL and HDL levels are crucial, as high LDL levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, while higher HDL levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
Risks Associated with High Cholesterol
Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to several serious health issues, primarily affecting the cardiovascular system. The risks include:
Heart Disease
High levels of LDL cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, which restricts blood flow.
Stroke
Increased cholesterol levels can result in blood clots, which may block blood flow to the brain, causing a stroke.
Heart Attack
When arteries become severely narrowed or blocked due to cholesterol buildup, the risk of heart attack significantly rises. Managing cholesterol levels is vital to reducing these risks and promoting heart health.
Cholesterol Level Testing
Regular cholesterol testing is essential for monitoring heart health. The most common method of testing is through a lipid panel, which measures total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. Here’s what you need to know about the testing process:
Preparation
Patients are usually advised to fast for 9-12 hours prior to the test to ensure accurate measurements.
Blood Sample
A healthcare professional draws blood, typically from a vein in the arm.
Analysis
The sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, where cholesterol levels are measured and results are generated.
Frequency of Testing
Adults should have their cholesterol levels checked at least every four to six years, or more frequently if at high risk for heart disease.Understanding cholesterol levels and their implications can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining heart health and overall wellness.
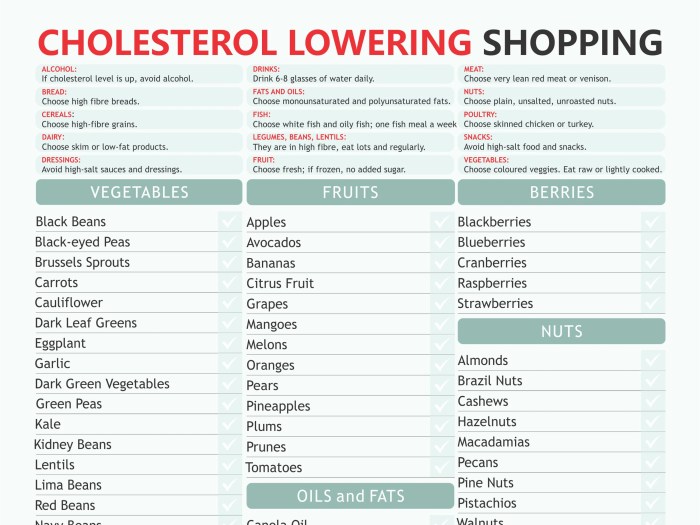
Foods that Help Lower Cholesterol
Eating the right foods can play a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. Various foods not only help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) but also support overall heart health. Incorporating these foods into your diet can lead to significant improvements in your cholesterol numbers and contribute to a healthier lifestyle.A variety of foods are recognized for their ability to help reduce cholesterol levels, primarily due to their nutrient composition.
Below, you will find a list of foods known to effectively lower cholesterol, along with explanations of how they contribute to heart health.
List of Cholesterol-Lowering Foods
The following foods are noteworthy for their cholesterol-lowering properties:
- Oats: Rich in soluble fiber, oats contain beta-glucan, which forms a gel-like substance in the gut. This gel helps trap cholesterol and its precursors, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream.
- Barley: Like oats, barley is high in soluble fiber. Regular consumption of barley has been associated with a decrease in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels.
- Beans and Legumes: These foods are excellent sources of soluble fiber. Varieties such as black beans, kidney beans, and lentils can lower cholesterol and promote heart health, thanks to their high fiber content.
- Fruits: Fruits like apples, pears, and citrus fruits are rich in pectin, a type of soluble fiber that lowers cholesterol levels. These fruits also provide antioxidants that support cardiovascular health.
- Nuts: Nuts, particularly almonds and walnuts, are high in healthy fats and fiber. They help improve cholesterol levels by reducing LDL cholesterol and increasing beneficial HDL cholesterol.
- Fatty Fish: Fish such as salmon and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can lower triglycerides and promote overall heart health. Regular intake of fatty fish can improve cholesterol profiles significantly.
- Avocado: This fruit is loaded with monounsaturated fats, which can lower bad cholesterol levels while raising good cholesterol. Its creamy texture makes it a versatile addition to many dishes.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Using it in place of saturated fats can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Role of Soluble Fiber in Cholesterol Reduction
Soluble fiber plays a significant role in lowering cholesterol levels. By absorbing water and forming a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, soluble fiber binds to cholesterol and bile acids. This process aids in their excretion from the body. Increased intake of soluble fiber leads to a reduction in the overall cholesterol that circulates in the bloodstream. Foods that are abundant in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and certain fruits, are effective in this capacity.
For instance, a daily intake of 5 to 10 grams of soluble fiber can lead to a reduction in LDL cholesterol by 5% to 10%.
“Incorporating soluble fiber into your diet can be a game changer for cholesterol management.”
Examples of Healthy Fats That Improve Cholesterol Levels
Not all fats are created equal, and certain types of fats can actually benefit heart health by improving cholesterol levels. Healthy fats, when consumed in moderation, can help maintain a balanced and heart-healthy diet.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Found in olive oil, avocados, and various nuts, these fats can lower LDL cholesterol while boosting HDL cholesterol. Swapping saturated fats for monounsaturated fats is a heart-healthy choice.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseeds, are beneficial in lowering triglyceride levels. They are essential for overall heart health and play a role in reducing inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Specific to fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, these fats not only lower LDL cholesterol but also reduce blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can contribute to better cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Making informed dietary choices is a vital step towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Incorporating Cholesterol-Lowering Foods in Daily Diet
Incorporating cholesterol-lowering foods into your daily diet doesn’t have to be complicated or bland. With a bit of planning, you can create delicious meals that not only taste great but also contribute to heart health. Here’s a practical approach to making these foods a regular part of your eating habits.Designing a daily meal plan that emphasizes cholesterol-lowering foods involves selecting ingredients that are rich in soluble fiber, healthy fats, and plant sterols.
A balanced meal plan can keep your meals exciting while maintaining your cholesterol levels in check. Here’s an example of a daily meal plan:
Sample Daily Meal Plan
This meal plan includes various foods known to lower cholesterol effectively.Breakfast:
- Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a sprinkle of ground flaxseeds.
- A cup of green tea.
Lunch:
- Quinoa salad with spinach, chickpeas, cherry tomatoes, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
- A side of carrot sticks.
Snack:
A small handful of almonds or walnuts.
Dinner:
- Grilled salmon with a side of steamed broccoli and sweet potato.
- A mixed green salad with avocado and olive oil dressing.
“A variety of colors on your plate often means a variety of nutrients.”
To maintain the health benefits of these foods, it’s essential to choose the right cooking methods. Here are some effective cooking techniques that help keep the nutrients intact while enhancing flavors:
Cooking Methods to Preserve Health Benefits, Foods to lower cholesterol
Utilizing the correct cooking methods can make a significant difference in retaining the nutritional value of cholesterol-lowering foods.
Steaming
This method helps retain water-soluble vitamins in vegetables, making it a great choice for greens like broccoli and spinach.
Grilling
For meats like salmon, grilling can enhance flavor without adding excess fat. This method also allows excess fat to drip away.
Sautéing
Using healthy oils, such as olive oil, in moderation while sautéing vegetables can enhance taste and provide beneficial fats.
Baking
Baking instead of frying can reduce the amount of unhealthy fats consumed, especially when preparing meals like sweet potatoes.
Grocery Shopping Tips for Cholesterol-Lowering Foods
When shopping for cholesterol-lowering options, it’s important to focus on fresh and whole foods while avoiding processed items. Here are some tips to guide your grocery list:
Choose whole grains
Look for products labeled as whole grain, such as whole wheat bread or brown rice.
Select healthy fats
Opt for oils like olive or avocado oil, and incorporate fatty fish like salmon or mackerel.
Stock up on fruits and vegetables
Aim for a variety of colors and types, focusing on those high in fiber such as apples, berries, and leafy greens.
Explore legumes
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of protein and fiber that can help lower cholesterol.
Be wary of labels
Watch out for added sugars and unhealthy fats in packaged foods, and prioritize natural, unprocessed items.
“Reading labels helps you make informed choices about what goes into your body.”
With these meal planning ideas, cooking methods, and shopping tips, incorporating cholesterol-lowering foods into your daily diet can be both enjoyable and beneficial for your health.
Additional Lifestyle Changes to Support Healthy Cholesterol
Source: etsystatic.com
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is not solely dependent on diet; lifestyle choices also play a crucial role. Incorporating regular exercise, managing weight, and utilizing stress reduction techniques can significantly influence your cholesterol levels. These changes can lead to a healthier heart and improve overall well-being.
Exercises that Help Lower Cholesterol Levels
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for improving cholesterol levels. Exercise helps raise high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as the “good” cholesterol, while lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol. Here are some effective exercises for cholesterol management:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are excellent for cardiovascular health.
- Strength training: Incorporating resistance exercises at least twice a week can help increase muscle mass, which boosts metabolism and cholesterol levels.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense activity, followed by rest, can improve cardiovascular fitness and cholesterol levels significantly.
Impact of Weight Management on Cholesterol
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for managing cholesterol. Excess weight can lead to higher levels of LDL cholesterol and lower levels of HDL cholesterol. Weight loss can reverse these trends and improve heart health. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of body weight can result in significant improvements in cholesterol levels.
“Every pound lost can help reduce LDL cholesterol and lower the risk of heart disease.”
Stress Reduction Techniques that Positively Influence Cholesterol
High-stress levels can negatively affect cholesterol levels by increasing the production of certain hormones that can raise cholesterol and blood pressure. Implementing stress reduction techniques can lead to better heart health. Consider the following methods:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can lower stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Yoga: This practice combines physical movement, meditation, and breathing exercises which can reduce stress levels effectively.
- Deep breathing exercises: Simple techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing can help activate the body’s relaxation response.
Integrating these lifestyle changes into daily routines can lead to better cholesterol management and enhance overall health.
Common Myths About Cholesterol and Diet

Source: batonrougeclinic.com
There are numerous misconceptions about cholesterol that can lead to confusion when it comes to dietary choices. Understanding these myths versus facts is crucial for making informed decisions that support heart health. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common myths associated with cholesterol and diet, separating fact from fiction.
Dietary Cholesterol Myths
One prevalent myth is that all cholesterol consumed through food significantly raises blood cholesterol levels. However, recent studies indicate that for most people, dietary cholesterol has a minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels. The body tends to regulate its cholesterol production and absorption, meaning that when dietary cholesterol intake increases, the body usually compensates by reducing its own production.
The relationship between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol levels is not as straightforward as previously believed.
Additionally, many people worry about consuming eggs due to their cholesterol content. Research has shown that for most individuals, eating eggs in moderation does not have a negative effect on heart health. Instead, they can be a part of a balanced diet due to their high-quality protein and essential nutrients.
Fats and Cholesterol Misconceptions
Another common misconception is that all fats are harmful and should be avoided to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. It is vital to distinguish between different types of fats. Trans fats and saturated fats are known to raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, while unsaturated fats can help improve cholesterol profiles.Incorporating healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish, can contribute positively to heart health.
Instead of fearing fats, it’s important to focus on the types of fats consumed.
Not all fats contribute to unhealthy cholesterol levels; understanding the right types can support heart health.
Plant Sterols and Stanols Effects
Plant sterols and stanols are naturally occurring substances found in plants that can aid in lowering cholesterol levels. They work by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines, thus reducing the overall cholesterol levels in the body. Foods fortified with plant sterols and stanols, such as certain margarines and yogurts, have been shown to effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels.Research suggests that consuming just 2 grams of plant sterols or stanols daily can lower LDL cholesterol by about 5 to 15 percent.
Including these foods as part of a cholesterol-lowering diet can be beneficial for heart health.
Integrating plant sterols and stanols into your diet can significantly contribute to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Monitoring Progress and Adjustments
Monitoring your cholesterol levels after making dietary changes is essential to ensure that your efforts are yielding positive results. Recognizing signs of improvement can help motivate you to stick with your cholesterol-lowering plan and make any necessary adjustments based on your test results. A proactive approach not only enhances your overall health but also allows you to fine-tune your diet for the best outcomes.Evaluating your progress involves understanding how your cholesterol numbers respond to the dietary adjustments you’ve made.
Regular cholesterol tests, typically recommended every 4-6 months for those managing their levels, play a vital role in this process. When reviewing your results, it’s important to look for trends in your LDL (bad cholesterol), HDL (good cholesterol), and total cholesterol levels. Positive changes might include a decrease in LDL levels and an increase in HDL levels. Adjusting your dietary habits based on these test results can lead to further improvements.
Signs of Improvement in Cholesterol Levels
Identifying positive changes in your cholesterol levels can be both encouraging and informative. Regular monitoring can reveal significant signs of improvement:
- Decrease in LDL cholesterol levels indicating a reduction of bad cholesterol in the bloodstream.
- Increase in HDL cholesterol levels demonstrating improved heart health.
- Overall reduction in total cholesterol levels showing the effectiveness of your dietary changes.
- Improvement in triglyceride levels suggesting better management of blood fat.
Adjustments Based on Cholesterol Test Results
Making dietary adjustments based on test results allows you to optimize your cholesterol management plan. If test results show that your LDL levels remain high despite following a cholesterol-friendly diet, consider the following strategies:
- Increase intake of soluble fiber by incorporating foods such as oats, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables.
- Add healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil while reducing saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy.
- Incorporate more omega-3 fatty acids by including fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines into your meals.
- Emphasize plant-based foods and whole grains while reducing processed and high-sugar foods that can contribute to unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Checklist for Maintaining a Cholesterol-Friendly Diet
To ensure your dietary adjustments are sustainable and effective, consider using a checklist that reinforces healthy eating habits:
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in every meal.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Limit saturated fat intake by opting for lean protein sources.
- Incorporate fatty fish into your diet at least twice a week.
- Use healthy oils such as olive or canola oil for cooking.
- Stay hydrated and opt for water over sugary drinks.
- Monitor your portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Keep a food diary to track your meals and feelings about your diet.
Regular monitoring and adjustments are key to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and promoting overall heart health.
Ending Remarks: Foods To Lower Cholesterol
In conclusion, the journey towards lower cholesterol levels doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By making informed dietary choices and including foods that help reduce cholesterol, you can greatly enhance your health and well-being. Remember to pair these dietary changes with other lifestyle adjustments, and you’ll be well on your way to a healthier heart and a vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common foods that lower cholesterol?
Common foods include oats, beans, nuts, fatty fish, and olive oil.
How quickly can I see changes in my cholesterol levels?
You may see improvements in cholesterol levels within a few weeks of adopting a healthier diet.
Do I need to avoid all fats to lower cholesterol?
No, healthy fats like those found in avocados and nuts can actually help improve cholesterol levels.
Can I lower my cholesterol without medication?
Yes, many people can manage their cholesterol levels through diet and lifestyle changes alone.
Is it necessary to completely eliminate red meat to lower cholesterol?
No, moderation is key; lean cuts can be included in a heart-healthy diet.