Heart disease prevention tips set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers valuable insights into maintaining a healthy heart. As one of the leading causes of death worldwide, understanding heart disease and implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial for everyone. This guide explores the importance of nutrition, physical activity, stress management, and regular health screenings, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take charge of your heart health.
From dissecting the anatomy of the heart to outlining the essential lifestyle adjustments we can make, this overview highlights how simple changes can lead to significant improvements in cardiovascular well-being. Whether it’s adopting a heart-healthy diet or quitting smoking, understanding the various factors that contribute to heart disease is the first step towards a healthier future.
Understanding Heart Disease

Source: publicdomainpictures.net
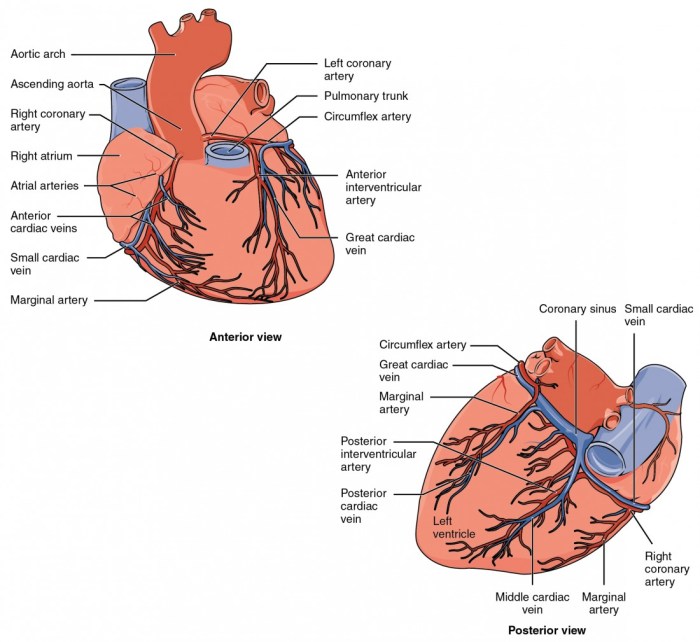
Heart disease is a broad term that encompasses various types of conditions affecting the heart’s structure and function. Understanding the anatomy of the heart and how these diseases affect it is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies. The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. When heart disease occurs, it can disrupt this vital process, leading to serious health complications.The heart consists of four main chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
Blood flows through these chambers in a systematic cycle. Heart disease can affect any part of this process, leading to conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valvular heart disease. These conditions may arise from various causes, including genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions.
Types of Heart Disease and Their Causes
Heart disease encompasses multiple types, each with distinct causes and implications for health. Understanding these can help individuals take proactive steps towards prevention. The most common types of heart disease include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This condition is caused by a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Risk factors include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
- Heart Failure: Occurs when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently, often due to long-standing high blood pressure or damage from a heart attack.
- Arrhythmias: These are irregular heartbeats that can occur due to a variety of factors, including stress, electrolyte imbalance, or underlying heart conditions.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Involves damage to one of the heart’s valves, which can be congenital or caused by infections or degenerative changes.
Role of Cholesterol and Blood Pressure in Heart Health
Cholesterol and blood pressure are two critical factors for maintaining heart health. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Conversely, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol is considered “good” cholesterol as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.Blood pressure is another vital aspect of heart health.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, forces the heart to work harder, leading to damage over time. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is essential to reducing the risk of heart disease. Regular monitoring of both cholesterol and blood pressure levels can aid in early detection and management of potential heart health issues.
Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress are key strategies for controlling cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and rich in fruits and vegetables, can significantly impact cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity helps to not only manage weight but also improve heart health. Additionally, understanding the importance of routine health check-ups can empower individuals to take charge of their heart health.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease: Heart Disease Prevention Tips
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally, making it crucial to understand the various risk factors that can contribute to its development. Identifying these factors allows individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention and management. This section delves into the common lifestyle choices, genetic influences, and medical conditions that can heighten the risk of heart disease.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Heart Disease
Several lifestyle choices can significantly impact heart health. Recognizing these factors can empower individuals to make healthier decisions. Key lifestyle contributors include:
- Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary behavior is a major risk factor. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages the blood vessels and can lead to the buildup of plaque, significantly increasing heart disease risk.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart failure and stroke.
- Stress: Chronic stress may lead to unhealthy habits such as poor eating and increased smoking or drinking, which can adversely affect heart health.
Genetics and Family History Impact
Genetics plays a significant role in heart disease risk. Individuals with a family history of heart disease are often at a heightened risk. This risk is not solely determined by genetic factors; rather, it encompasses a combination of inherited traits and lifestyle choices. For instance, if parents or siblings have heart disease, the likelihood increases due to shared genetics, lifestyle habits, and environmental influences.
“A family history of heart disease increases your risk, but it doesn’t mean you’re destined to face the same fate; lifestyle modifications can still make a difference.”
Medical Conditions Associated with Increased Risk
Certain medical conditions can exacerbate the likelihood of developing heart disease. Understanding these conditions is vital for early intervention and management. The following list highlights key medical issues associated with increased heart disease risk:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): This condition forces the heart to work harder, leading to damage of arteries and increased risk.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque formation in arteries, narrowing them and restricting blood flow.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease significantly, as high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels over time.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is linked to hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which contribute to heart disease risk.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: This condition is associated with cardiovascular disease, partly due to related hypertension and mineral imbalances.
Nutrition and Heart Health
Eating a heart-healthy diet is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing heart disease. A well-balanced diet helps manage cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and overall weight, making it a crucial factor in heart health. Understanding which foods nourish your heart and how to incorporate them into your daily meals can make a significant difference.A heart-healthy diet focuses on whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients.
This includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Adopting such dietary habits not only supports your heart but also enhances your overall well-being. Below are detailed food choices and a few recipe ideas that promote cardiovascular health.
Heart-Healthy Food Choices
Incorporating heart-healthy foods into your diet involves selecting items that are low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Here are some vital food groups and items to consider:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a rainbow of colors on your plate. Berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits are especially beneficial due to their high levels of antioxidants and vitamins.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grain bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats. These provide fiber, which is important for reducing cholesterol levels.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon and mackerel, as well as plant-based proteins such as beans, lentils, and nuts.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts, while reducing saturated and trans fats found in red meat and processed foods.
Heart-Healthy Recipes, Heart disease prevention tips
Simple recipes can help you create delicious meals that support heart health. Here are a couple of heart-healthy recipes that use beneficial ingredients: Quinoa Salad with Spinach and Avocado:This dish is loaded with fiber and healthy fats. In a bowl, mix cooked quinoa, fresh spinach, diced avocado, cherry tomatoes, and a dressing made of olive oil and lemon juice. Sprinkle with nuts for added crunch.
Salmon and Vegetable Stir-Fry:Pan-sear salmon fillets and serve them over a mix of sautéed broccoli, bell peppers, and carrots. Season with low-sodium soy sauce and ginger for a flavorful yet heart-healthy meal.
Importance of Portion Control and Mindful Eating
Portion control and mindful eating are pivotal in managing caloric intake and promoting heart health. Being mindful about what and how much you eat helps prevent overeating, which can lead to weight gain and increased cardiovascular risk. Understanding appropriate portion sizes is essential. Consider using smaller plates and bowls to help control servings naturally. Focus on listening to your body’s hunger cues rather than eating out of habit or boredom.
“Mindful eating involves being present during meals, savoring each bite, and appreciating the flavors and textures of food, which can lead to healthier eating habits.”
Adopting these strategies can significantly impact your heart health by ensuring you consume balanced meals without overindulging. By making informed choices about food and being mindful in your eating habits, you are taking vital steps towards heart disease prevention.
Physical Activity Recommendations

Source: publicdomainpictures.net
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing heart disease. Engaging in the right types and amounts of exercise can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular issues while improving overall physical and mental well-being. This section presents a structured approach to physical activity, tailored specifically for heart disease prevention.
Weekly Exercise Plan for Heart Health
A well-rounded weekly exercise plan should balance aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Here’s a sample schedule:
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Aerobic exercise (e.g., brisk walking, cycling) | 30 minutes |
| Tuesday | Strength training (e.g., bodyweight exercises, resistance bands) | 30 minutes |
| Wednesday | Yoga or stretching | 30 minutes |
| Thursday | Aerobic exercise (e.g., swimming, dancing) | 30 minutes |
| Friday | Strength training (e.g., free weights, machines) | 30 minutes |
| Saturday | Outdoor activities (e.g., hiking, playing sports) | 1 hour |
| Sunday | Rest or light activity (e.g., walking, gentle yoga) | As desired |
This plan includes a mix of aerobic activities to boost cardiovascular fitness, strength training to enhance muscular health, and flexibility exercises to improve mobility and prevent injuries.
Types of Exercise and Their Benefits
Different forms of exercise contribute uniquely to heart health. Understanding these benefits can help individuals choose their preferred activities:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as running, cycling, or swimming improve cardiovascular endurance and help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Strength Training: Exercises using weights or resistance bands increase muscle mass, boost metabolism, and improve insulin sensitivity, which is vital for heart health.
- Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Practices like yoga and tai chi enhance flexibility, improve balance, and reduce stress, all of which can indirectly support heart health.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest periods are effective for improving cardiovascular fitness and burning calories quickly.
Incorporating a variety of these exercises into your routine not only keeps workouts interesting but also addresses different aspects of physical health.
Maintaining Motivation for Regular Exercise
Staying motivated to exercise regularly can be challenging. Here are some strategies to help maintain enthusiasm and commitment to an exercise routine:
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable short-term and long-term fitness goals to track progress and celebrate milestones.
- Find a Workout Buddy: Exercising with a friend or family member can increase accountability and make workouts more enjoyable.
- Mix It Up: Vary your workouts by trying new exercises, classes, or outdoor activities to keep things fresh and engaging.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a journal or use fitness apps to monitor your workouts, which can provide motivation through visible progress.
- Reward Yourself: Set up a reward system for reaching your fitness goals, such as treating yourself to a new workout outfit or a relaxing spa day.
Implementing these tips can help foster a sustainable and enjoyable exercise routine that supports heart health over the long term.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress plays a significant role in heart health, influencing both the cardiovascular system and overall wellness. Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and other heart disease risk factors. Understanding the connection between stress and heart disease is essential for everyone looking to maintain a healthy heart.Stress activates the body’s “fight or flight” response, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Over time, these physiological changes can contribute to the development of heart disease. Keeping stress in check is not just about feeling better—it’s an important part of protecting your heart. Implementing effective stress management techniques can significantly lower your risk of heart-related issues.
Incorporating Relaxation and Mindfulness
Mindfulness and relaxation practices are powerful tools for managing stress. These techniques can help individuals stay grounded, maintain perspective, and enhance emotional resilience. Here are some effective methods:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Engaging in deep breathing can help calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety. A simple technique involves inhaling deeply through the nose, holding for a few seconds, and exhaling slowly through the mouth.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This method involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups, which can alleviate physical tension and promote relaxation.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Spending a few minutes each day focusing on the present moment can reduce stress and improve mental clarity. Apps and guided sessions are available for beginners.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical movement with mindfulness and can enhance flexibility, strength, and relaxation. They are especially beneficial for heart health.
Integrating these practices into your daily routine can provide a sense of calm and improve your overall health. Simple adjustments, like setting aside a few minutes each day for these activities, can make a profound difference.
Benefits of Hobbies and Social Connections
Engaging in hobbies and maintaining social connections are vital for heart health and stress reduction. Hobbies provide a break from routine and can significantly elevate mood. Activities such as painting, gardening, or playing a musical instrument promote relaxation and can lower stress levels.Social connections, on the other hand, foster a sense of belonging and support. Research shows that individuals with strong social networks tend to experience lower levels of stress and better overall health.
Here’s how they contribute to heart health:
- Emotional Support: Friends and family provide a cushion during tough times, helping to mitigate stress and anxiety.
- Shared Activities: Engaging in physical activities with friends, like walking or biking, can enhance motivation and enjoyment.
- Increased Happiness: Positive interactions and shared experiences can boost mental health, which is closely linked to heart health.
Incorporating hobbies and nurturing social connections into daily life are essential strategies for reducing stress and promoting heart health. Creating time for these activities can lead to a more balanced, fulfilling life.
Smoking and Heart Disease
Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing heart disease, contributing to various cardiovascular issues. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage blood vessels, raise heart rate, and decrease the amount of oxygen in the blood, leading to an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Understanding the impact of smoking on heart health is crucial for effective prevention and management of heart disease.
Effects of Smoking on Cardiovascular Health
Smoking negatively affects cardiovascular health in several ways. It leads to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which narrows them and restricts blood flow. This can result in atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks. Additionally, smoking raises blood pressure and increases heart rate, putting more strain on the heart. The carbon monoxide in cigarette smoke reduces the amount of oxygen that blood can carry, further stressing the heart and contributing to its overall decline.
Strategies for Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is a crucial step towards improving heart health. There are various strategies that can help individuals kick the habit:
- Set a Quit Date: Choose a specific date to stop smoking and prepare for it mentally and emotionally.
- Seek Support: Engage with support groups or professional counseling to stay motivated and accountable.
- Use Nicotine Replacement Therapy: Consider patches, gum, or lozenges to manage withdrawal symptoms.
- Identify Triggers: Recognize and avoid situations that trigger the urge to smoke, such as social events or stressful situations.
- Stay Active: Engage in physical activities to distract from cravings and reduce stress.
Resources for Support
Numerous resources are available to assist individuals in their journey to quit smoking. Local health departments often provide programs and materials. The National Cancer Institute offers a quitline, while various mobile apps and websites provide guidance and tracking tools. Accessibility to these resources can significantly boost the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
Benefits of Being Smoke-Free
The benefits of quitting smoking extend beyond improved cardiovascular health. When an individual stops smoking, the heart begins to heal almost immediately. Within just 20 minutes, heart rate drops; after a few months, the risk of heart disease decreases significantly.
“Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of heart disease by 50% within one year.”
Additionally, being smoke-free improves overall health, increases energy levels, and enhances the quality of life. Long-term, the chances of developing various chronic diseases, including heart disease, drastically decrease.
Regular Health Screenings
Source: amazonaws.com
Regular health screenings play a crucial role in the early detection and prevention of heart disease. They help identify potential risk factors and existing conditions before they escalate into serious health issues. Staying proactive with your heart health can significantly improve outcomes and enhance your overall well-being.Essential health screenings are designed to assess various aspects of cardiovascular health, enabling individuals to make informed decisions regarding their lifestyle and medical care.
The following key tests are integral to monitoring heart health:
Essential Health Screenings for Heart Health
These screenings are vital for understanding your heart’s condition and overall risk for heart disease. They include:
- Blood Pressure Measurement: Regular checks help detect hypertension early, an important risk factor for heart disease.
- Cholesterol Levels: A lipid panel measures total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides, informing you of your heart disease risk.
- Blood Glucose Testing: High blood sugar can increase the risk of heart disease; regular checks help manage and prevent diabetes.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Monitoring BMI helps assess weight-related risks, including obesity, which can affect heart health.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test assesses the heart’s electrical activity, helping detect arrhythmias or signs of past heart attacks.
- Stress Test: Conducted under controlled conditions, this test evaluates how the heart responds to physical exertion.
The frequency of these screenings can vary based on individual health status and risk factors. Here’s a recommended timeline for regular check-ups and tests related to heart health:
Recommended Timeline for Health Screenings
Establishing a consistent schedule for heart health screenings is essential. The following timeline can serve as a guideline:
- Annually: Blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and BMI should be checked every year for most adults.
- Every 3 to 5 years: Blood glucose testing should be conducted, particularly for those over 45 or at high risk.
- Every 5 years: A comprehensive lipid panel is recommended for adults over 20, or more frequently if you have high cholesterol.
- As advised: An ECG or stress test may be recommended based on personal health history or symptoms.
Interpreting the results of heart health screenings is crucial for understanding your risks and taking appropriate actions. Here are key points to consider when reviewing results:
Interpreting Heart Health Screening Results
Understanding your screening results empowers you to make informed decisions about your heart health. Here’s what to look for:
- Blood Pressure: Normal is below 120/80 mmHg. Higher readings indicate potential hypertension, requiring lifestyle changes or medication.
- Cholesterol Levels: Total cholesterol should be below 200 mg/dL. Pay attention to LDL (bad cholesterol), which should be less than 100 mg/dL, while HDL (good cholesterol) should be 60 mg/dL or higher.
- Blood Glucose: Fasting levels should be below 100 mg/dL. Higher levels may indicate prediabetes or diabetes.
- BMI: A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy. Values above indicate overweight or obesity, increasing heart disease risks.
“Regular health screenings are your first line of defense against heart disease, helping you stay informed and proactive.”
By adhering to a structured screening schedule and effectively interpreting your results, you can take significant steps toward maintaining a healthy heart and preventing disease.
Community and Support Systems
Community plays a vital role in promoting heart health awareness and prevention strategies. Engaging with local programs not only fosters education around heart disease but also creates a supportive environment where individuals can share experiences and encourage each other toward healthier lifestyles. Community initiatives often provide resources that individuals may not access on their own, making them essential in the fight against heart disease.Various community programs are designed to enhance heart health awareness.
Here are some examples of initiatives that demonstrate the effectiveness of collective action in preventing heart disease:
- Health fairs that offer free screenings, educational workshops, and access to healthcare professionals help individuals understand their risk factors.
- Community-based exercise programs, such as walking clubs or group fitness classes, promote physical activity while fostering relationships among participants.
- Nutrition workshops that teach cooking skills and meal planning provide valuable information on heart-healthy eating.
- Fundraising events, such as heart walks or runs, raise awareness and funds for heart health research, bringing the community together for a common cause.
Support Groups for Individuals at Risk of Heart Disease
Support groups serve as a lifeline for individuals at risk of heart disease. They provide a safe space for people to share their fears, challenges, and successes. These groups often include a mix of educational content and emotional support, creating a holistic approach to heart health management. The importance of family involvement in heart disease prevention strategies cannot be overstated.
Family members can influence lifestyle choices significantly, making their participation crucial. Here are key points on the role of family in heart disease prevention:
- Support from family encourages healthier eating habits and regular physical activity. When families engage in these behaviors together, it helps to normalize them.
- Open communication about heart health can foster a culture of awareness and proactive health management within the family unit.
- Family members can help monitor each other’s health through regular check-ins, ensuring that everyone stays informed about their risk factors.
- Shared goals, such as participating in community events or challenges, can create motivation and strengthen family bonds.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, prioritizing heart disease prevention is a vital step towards enhancing not just longevity but also quality of life. By embracing healthy habits, staying active, managing stress, and regularly checking in with healthcare professionals, we take proactive measures to protect our hearts. Remember, every small effort counts, and with the right knowledge and support, we can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease and enjoy a vibrant, active lifestyle.
FAQ Resource
What are the most common signs of heart disease?
Common signs include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat.
How often should I get screened for heart disease?
It’s recommended to have health screenings at least once a year, but consult your doctor for personalized advice.
Can heart disease be reversed?
While it may not be fully reversible, lifestyle changes can significantly improve heart health and reduce symptoms.
How does stress affect heart health?
Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and unhealthy habits, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Are there specific diets that help prevent heart disease?
Yes, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, like the Mediterranean diet, are beneficial for heart health.