Intermittent fasting guide opens the door to a transformative approach to eating that has captured the attention of health enthusiasts worldwide. This method, which alternates between periods of eating and fasting, is not a diet but a lifestyle choice that encourages mindful eating and a deeper understanding of our bodies. With various methods like the 16/8 approach and the 5:2 diet, intermittent fasting offers flexibility while promising numerous health benefits such as improved metabolism and weight management.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the different types of intermittent fasting, explore their unique benefits, and provide practical steps for getting started. Whether you’re a busy professional or a fitness enthusiast, there’s a fasting method tailored to suit your lifestyle, making this an accessible and appealing option for anyone looking to enhance their well-being.
Introduction to Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent Fasting Guide
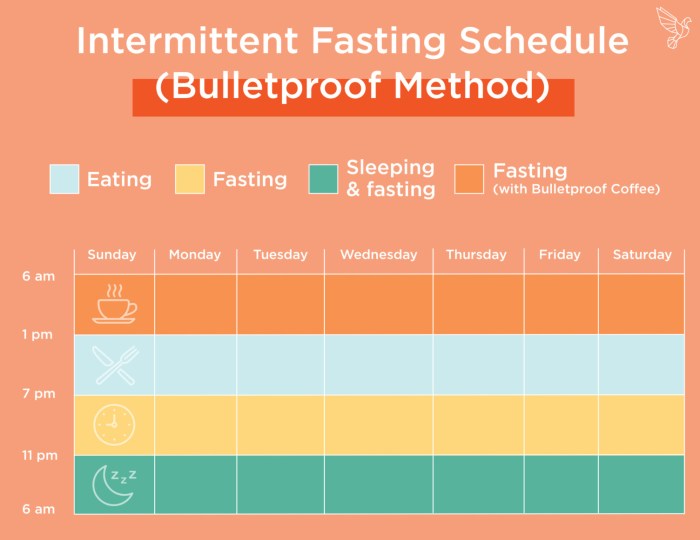
Source: bulletproof.com
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. Unlike traditional diets that focus on what to eat, intermittent fasting emphasizes when to eat. This approach to eating has deep historical roots, being practiced in various forms by cultures throughout history for spiritual, health, and survival reasons. From ancient hunter-gatherer societies to modern-day health enthusiasts, the concept has evolved but remains centered around the idea of timed eating.There are several popular methods of intermittent fasting, each with its own structure and guidelines.
Understanding these methods can help individuals select the one that best suits their lifestyle and goals. The most commonly practiced forms include the 16/8 method, where individuals fast for 16 hours a day and eat during an 8-hour window; the 5:2 diet, which involves eating normally for five days of the week while restricting calorie intake to about 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days; and alternate day fasting, which alternates between fasting days and non-fasting days.
Overview of Intermittent Fasting Methods
Each method of intermittent fasting has its unique benefits and can cater to different lifestyles. Understanding these methods not only helps in selecting a suitable approach but also highlights the flexibility of intermittent fasting as a dietary strategy. Here’s a closer look at the most popular methods:
- 16/8 Method: This method involves fasting for 16 hours and limiting eating to an 8-hour window, often making it easier to integrate into daily routines. For example, one might choose to eat between noon and 8 PM, skipping breakfast but enjoying lunch and dinner.
- 5:2 Diet: In this approach, individuals eat normally for five days of the week while significantly reducing caloric intake on two non-consecutive days. This method allows for flexibility in meal planning and doesn’t require daily fasting.
- Alternate Day Fasting: This method alternates between days of regular eating and fasting days. On fasting days, one might consume very few calories, creating a significant calorie deficit over the week.
Potential Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is associated with a range of health benefits that extend beyond weight loss. Many studies suggest that engaging in intermittent fasting can lead to improvements in metabolic health, reduced inflammation, and even potential longevity benefits.
“Intermittent fasting can trigger cellular repair processes and promote metabolic changes that improve health.”
Some of the key benefits include:
- Weight Loss: By reducing overall caloric intake and enhancing metabolic rate, intermittent fasting can be an effective tool for weight management.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: IF can lower insulin levels and improve insulin sensitivity, which may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Health: Intermittent fasting may lead to reductions in blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammatory markers, contributing to overall heart health.
- Cognitive Benefits: Some research suggests that intermittent fasting may support brain health, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Enhanced Longevity: Animal studies have shown that fasting can extend lifespan, and while more research in humans is needed, the potential for longevity is intriguing.
Different Types of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a popular approach to eating that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Various methods cater to different lifestyles and preferences, making IF accessible to many. Understanding these methods can help individuals choose the one that aligns best with their routines and health goals.Intermittent fasting can take several forms, each with its unique structure and benefits.
Here’s a breakdown of some widely practiced types, including the Warrior Diet and Eat-Stop-Eat, examining their characteristics and suitability for various lifestyles.
Overview of Intermittent Fasting Methods
Several methods of intermittent fasting offer flexibility, allowing individuals to choose a fasting routine that fits their lifestyle. The following table summarizes the key features of different intermittent fasting methods:
| Method | Fasting Period | Eating Window | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16/8 Method | 16 hours | 8 hours | Great for beginners and those with a structured daily schedule. |
| 5:2 Diet | 2 non-consecutive days of 500-600 calories | Normal eating on other days | Suitable for those who prefer to eat normally most days but can handle calorie restriction occasionally. |
| Eat-Stop-Eat | 24 hours | Normal eating on non-fasting days | Good for individuals who can manage longer fasting periods without adverse effects. |
| Warrior Diet | 20 hours of undereating | 4-hour eating window | Ideal for those who prefer a more flexible approach with smaller meals during the day. |
| Alternate Day Fasting | 24 hours of fasting on alternate days | Normal eating on non-fasting days | Recommended for individuals looking for a more intensive fasting plan. |
“Choosing the right intermittent fasting method is crucial for sustained adherence and success.”
Each intermittent fasting method has its unique characteristics, making them suitable for a variety of personal preferences and lifestyles. For instance, the 16/8 method is often favored by those with a consistent daily routine, as it allows for a balanced eating schedule. On the other hand, the Eat-Stop-Eat method may appeal to individuals who are comfortable with longer fasting periods and can tolerate the effects of a full day without food.The Warrior Diet, characterized by a day of undereating followed by a significant meal at night, suits those who prefer to focus on nutrient-dense foods during a limited time frame.
Individuals who thrive on structure might find the 5:2 Diet appealing, as it allows for moderation throughout the week.Ultimately, selecting the right intermittent fasting method involves considering one’s lifestyle, preferences, and health goals. Adapting to a fasting plan that feels comfortable and sustainable is essential for long-term success.
Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting

Source: advanced-nutrition-and-health.com
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained immense popularity not only for its weight loss benefits but also for its positive effects on overall health. Emerging scientific studies continue to unveil the multifaceted health benefits of this dietary approach, demonstrating its potential to enhance various aspects of well-being. Intermittent fasting can act as a powerful tool for weight management and improving metabolic health, while also contributing to increased longevity.
Research has shown that IF can help reduce body weight and improve metabolic markers such as insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels. Additionally, it may promote cellular repair processes and reduce inflammation, which are crucial for long-term health.
Scientific Studies Supporting Health Benefits
Numerous studies underscore the efficacy of intermittent fasting in promoting health. Here are some key findings:
- A study published in the
-New England Journal of Medicine* highlighted that intermittent fasting might lead to a reduction in body fat and improved cholesterol levels. - Research from the
-Journal of Translational Medicine* found that participants practicing IF showed significant improvements in insulin sensitivity, contributing to metabolic health. - A review in
-Cell Metabolism* suggested that fasting could enhance the body’s stress resistance and promote longevity by activating various cellular repair mechanisms.
Impact on Weight Loss and Metabolic Health
Intermittent fasting simplifies eating patterns, which can lead to decreased calorie intake without the need for strict dieting. This approach not only fosters weight loss but also enhances metabolic health in several ways:
- Weight Loss: By reducing the eating window, IF helps individuals consume fewer calories, leading to weight loss. Studies have shown participants can lose 3-8% of their body weight over a period of 3-24 weeks.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Fasting periods allow insulin levels to drop, which facilitates fat burning. Enhanced insulin sensitivity reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Enhanced Fat Oxidation: Research indicates that fasting promotes the utilization of stored fat for energy, contributing to healthier body composition.
Examples of Personal Health Improvements
Many individuals have reported transformative health benefits after adopting intermittent fasting.
“Since incorporating intermittent fasting into my routine, I have lost 30 pounds and my energy levels have significantly increased.”
Jamie, age 34
“After three months of intermittent fasting, my doctor noted a remarkable decrease in my blood sugar levels, which I struggled with for years.”
Mark, age 50
These personal testimonies highlight the potential of intermittent fasting to catalyze not only weight loss but also significant improvements in metabolic health, reinforcing the positive outcomes supported by scientific evidence.
How to Begin Intermittent Fasting
Starting an intermittent fasting regimen can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can become a manageable and rewarding part of your lifestyle. This guide will provide you with a clear roadmap to getting started, ensuring that you set realistic goals and track your progress effectively.Establishing a successful intermittent fasting plan requires preparation and a thoughtful approach. By understanding your own needs and how fasting fits into your daily routine, you can create a sustainable fasting schedule that works for you.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you initiate your intermittent fasting journey.
Step-by-Step Guide
To kick off your intermittent fasting routine, follow these steps:
1. Choose Your Fasting Method
Understand the different types of intermittent fasting (such as the 16/8 method, 5:2 method, or alternate-day fasting) and choose one that aligns with your lifestyle.
2. Set Realistic Goals
Rather than aiming for drastic weight loss or health changes overnight, set achievable milestones. A goal of losing 1-2 pounds per week or improving your energy levels can be more motivating.
3. Create a Fasting Schedule
Based on your chosen method, Artikel a clear daily or weekly fasting schedule. Consistency is key, so picking a time frame that fits well within your daily routine will help you stick to it.
4. Plan Your Meals
Focus on nutritious, balanced meals during your eating windows. This helps ensure you’re getting the right nutrients and keeps hunger at bay during fasting periods.
5. Stay Hydrated
Water, herbal teas, and black coffee are great options to stay hydrated during fasting hours. This can help curb hunger and keep your energy levels up.
6. Listen to Your Body
As you start fasting, be attentive to how your body responds. Adjust your fasting periods if necessary and prioritize your comfort and well-being.
Monitoring Progress
Tracking your progress is crucial to ensure that your intermittent fasting plan is working effectively. Regularly assessing how you feel and any changes in your weight or health markers can help you stay motivated and make necessary adjustments.
Journaling
Keep a journal to note your daily experiences, energy levels, and hunger cues. This can provide insights into what works best for you.
Use Apps
Consider using apps designed for intermittent fasting that help track your fasting and eating windows, as well as your progress over time.
Checklist for Beginners
To ease into your first fasting period, use this checklist to prepare:
Research
Familiarize yourself with different fasting methods and their benefits.
Consult a Professional
If you have any health concerns or conditions, consult a healthcare provider before starting.
Set Up Your Kitchen
Stock up on healthy foods that you’ll enjoy during your eating windows. Ditch junk food to reduce temptation.
Inform Others
Tell family and friends about your fasting plan so they can support you and understand any changes in your routine.
Plan Your First Fast
Decide on the start date and have a plan for your first fasting period mapped out.
Prepare for Challenges
Understand that the initial days may be tough. Have strategies in place to deal with hunger cravings and distractions.By following these guidelines and being mindful of your body’s responses, you’ll be well on your way to successfully integrating intermittent fasting into your lifestyle.
Challenges and Solutions in Intermittent Fasting
Starting intermittent fasting can be an exciting journey towards better health, yet it often comes with its share of challenges. As you transition into this new eating pattern, you might face hurdles like hunger pangs and social situations that disrupt your fasting routine. Recognizing these challenges and finding practical solutions can significantly enhance your fasting experience and help you stay committed to your health goals.Hunger is one of the most common challenges individuals encounter when starting intermittent fasting.
The body’s adaptation to new eating windows can lead to feelings of emptiness and cravings. Additionally, social situations, such as dinner parties or outings with friends, can create pressure to eat when you’re not scheduled to, making it difficult to stick to your fasting plan. However, these obstacles can be managed effectively with the right strategies.
Strategies to Overcome Common Challenges
It’s vital to have a toolkit of strategies to manage the typical hurdles of intermittent fasting. Here are some practical solutions:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help curb hunger and keep you feeling full. Herbal teas and black coffee are also great options during fasting periods.
- Mindful Eating: When it’s time to eat, focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide lasting energy, such as proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich vegetables.
- Plan Social Events: If you know you’ll be attending a social gathering, try to eat a healthy meal before going or choose a time that aligns with your fasting schedule.
- Communicate Your Goals: Let friends and family know about your fasting plan. This way, they can support your efforts and offer understanding during social situations.
- Keep Busy: Engage in activities during fasting periods to distract yourself from cravings and keep your mind off food.
Keeping Motivation High During Fasting Periods
Maintaining motivation is essential for long-term success in intermittent fasting. Here are some effective strategies to help keep your spirits up during fasting periods:
- Set Clear Goals: Define your reasons for starting intermittent fasting, whether for weight loss, improved mental clarity, or health benefits. Write these down and refer back to them often.
- Track Progress: Utilize a journal or an app to monitor your fasting schedule, meals, and any physical changes. Seeing your progress can be a huge motivator.
- Join a Community: Engage with others who practice intermittent fasting through online forums or local groups. Sharing experiences and tips can boost morale and provide encouragement.
- Remind Yourself of Benefits: Keep a list of the health benefits you’re experiencing, such as increased energy levels, better digestion, or weight loss, to remind yourself why you started.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge and reward yourself for sticking to your fasting plan, whether it’s treating yourself to new workout gear or enjoying a favorite meal after your fasting window.
Intermittent Fasting and Nutrition
![Intermittent Fasting 101 – Beginners Guide [Updated in 2025] Intermittent fasting guide](https://health.gajikerja.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Intermittent-Fasting-101-Beginners-Guide.jpg)
Source: fastingapps.com
Nutrition plays a crucial role during the eating windows in intermittent fasting, as it directly impacts the effectiveness of the fasting regimen. While fasting itself allows the body to rest and repair, the food consumed during eating periods determines how well the body utilizes this fasting period for health benefits. Proper nutrition can enhance energy levels, promote better metabolic health, and support the overall goals associated with intermittent fasting.A well-planned diet not only aids in maintaining energy levels but also ensures that the body receives the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning.
Focusing on whole, nutrient-rich foods during eating windows is essential to support the body efficiently through fasting. This involves selecting foods that are high in vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, while minimizing processed foods and sugars.
Recommended Food Choices and Meal Planning
Selecting the right foods is vital for a successful intermittent fasting experience. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help in achieving health goals and maintaining energy levels throughout the fasting period. Below are some recommended food choices:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins like lentils and beans.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole-grain bread provide sustained energy.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fresh produce like berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables are packed with vitamins and fiber.
- Dairy or Alternatives: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and plant-based alternatives rich in calcium and protein.
To effectively support intermittent fasting, meal planning can help ensure a balanced intake of these nutrients. Here are some strategies for meal planning:
1. Batch Cooking
Prepare large portions of healthy meals in advance to save time and avoid unhealthy snacking.
2. Balanced Meals
Aim for meals that combine proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates to keep you full and satisfied.
3. Mindful Eating
Focus on eating slowly and enjoying your meals, which can help prevent overeating.
4. Hydration
Drink plenty of water during both fasting and eating windows to stay hydrated and aid digestion.
Sample Meal Plan for a Week
A structured meal plan can help streamline your eating windows and ensure nutritional balance. Below is a sample meal plan for a week that aligns with a common 16:8 intermittent fasting schedule, where eating occurs within an 8-hour window.
| Day | Breakfast (12 PM) | Lunch (3 PM) | Dinner (7 PM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-grain toast | Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and avocado | Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli |
| Tuesday | Greek yogurt with berries and nuts | Turkey wrap with lettuce, tomato, and hummus | Zucchini noodles with marinara sauce and meatballs |
| Wednesday | Oatmeal topped with banana and almond butter | Lentil soup with whole-grain bread | Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables over brown rice |
| Thursday | Smoothie with spinach, banana, and protein powder | Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, and feta | Grilled shrimp with asparagus and sweet potato |
| Friday | Chia seed pudding with coconut milk and mango | Caprese salad with tomatoes, mozzarella, and basil | Stuffed bell peppers with ground turkey and quinoa |
| Saturday | Whole-grain pancakes with berries and honey | Chicken stir-fry with vegetables | Baked cod with cauliflower rice and green beans |
| Sunday | Breakfast burrito with eggs, black beans, and salsa | Roasted vegetable and hummus platter | Grilled steak with a side of mixed green salad |
This meal plan is designed to provide a variety of foods that are nutritious and satisfying, helping to make the intermittent fasting experience enjoyable and effective. Remember, individual preferences and nutritional needs can vary, so adjust the plan accordingly to meet your personal health goals.
Intermittent Fasting for Specific Populations
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity among various demographics, yet it’s essential to consider how it may impact specific populations differently. Understanding these nuances is crucial for individuals who fall into categories such as athletes, pregnant women, and those with certain health conditions. Each group has unique needs and considerations that should guide their approach to fasting.Different populations can experience varied effects from intermittent fasting, which can be attributed to their specific physiological needs and health statuses.
For instance, athletes may require more energy and nutrients to support their performance, while pregnant women need to ensure they meet their nutritional requirements for both themselves and their developing fetus. Meanwhile, individuals with health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, need to be particularly cautious when implementing fasting protocols.
Athletes and Intermittent Fasting, Intermittent fasting guide
Athletes often have higher caloric and nutritional demands due to their active lifestyles. When considering intermittent fasting, it’s crucial to maintain energy levels while optimizing performance. Here are some key considerations for athletes:
- Timing of meals: Athletes may benefit from having their eating window align with training sessions to fuel workouts effectively.
- Quality of food: Emphasizing nutrient-dense foods during eating periods can help meet the increased energy needs.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential, especially during fasting hours, to prevent dehydration during intensive training.
Athletes should also monitor their performance and recovery closely. If they notice a decline in their training efficacy or energy levels, it may be necessary to adjust their fasting approach or consult a nutrition expert.
Pregnant Women and Intermittent Fasting
Pregnancy requires careful consideration of dietary practices due to the nutritional needs of both the mother and the developing baby. Intermittent fasting may not be suitable for all pregnant women. Here are important guidelines to consider:
- Nutritional intake: Pregnant women should ensure they are getting adequate calories and nutrients, focusing on vitamins and minerals that support fetal development.
- Consultation with healthcare providers: It’s essential for pregnant women to discuss any fasting plans with their obstetrician or a registered dietitian.
- Listening to the body: If fasting leads to fatigue or dizziness, it should be reconsidered or modified.
Fasting during pregnancy can lead to risks if not properly managed, thus professional guidance is highly recommended.
Individuals with Health Conditions and Intermittent Fasting
For those with health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, or eating disorders, intermittent fasting must be approached with caution. Here are several considerations:
- Blood sugar management: Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels closely, as fasting can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose levels.
- Medication timing: Understanding the timing of medications is crucial, as fasting may necessitate adjustments in dosing schedules.
- Professional oversight: It is vital to work with healthcare professionals to develop a safe fasting plan that accommodates specific health needs.
Careful planning and continuous monitoring are essential for individuals with health conditions to ensure that fasting does not pose additional health risks.
“Individual requirements vary significantly; therefore, personalized approaches to intermittent fasting are necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness.”
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Fasting
Monitoring your progress during intermittent fasting is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and ensuring it aligns with your health goals. By keeping track of your experiences and results, you can make informed adjustments that enhance your fasting regimen. Consistent monitoring allows you to identify what works for you and what might need tweaking.Using tools such as journaling or specific apps can provide valuable insights into your fasting journey.
These methods not only help you document your food intake and fasting windows but also encourage reflection on how you feel throughout the process. This is essential in assessing the effectiveness of your fasting approach and knowing when to make necessary changes.
Methods for Tracking Progress
Establishing a reliable system to monitor your fasting journey is important for long-term success. Here are some effective methods for tracking your progress:
- Journaling: Writing down your daily experiences, including fasting durations, meals, and energy levels, can help you recognize patterns and identify what works best.
- Mobile Apps: There are various apps designed specifically for intermittent fasting that allow you to log your eating windows, weight, and even hydration levels.
- Body Measurements: Regularly tracking your weight, waist circumference, and body fat percentage can provide tangible evidence of your progress and help you stay motivated.
- Mood and Energy Levels: Keeping a record of how you feel during fasting periods can indicate whether the current approach suits your lifestyle and well-being.
Assessing Effectiveness and Making Adjustments
Evaluating your fasting regimen’s effectiveness involves looking at both physical and mental changes. Consider the following indicators to assess whether it’s time to make adjustments:
- Physical Changes: Noticeable changes in weight, body composition, or energy levels can signal the effectiveness of your fasting approach.
- Mental Clarity: An increase in focus and cognitive function often indicates that your body is responding well to fasting.
- Hunger Cues: If persistent hunger or cravings are affecting your daily life, it may be time to reevaluate your fasting schedule.
- Health Indicators: Regular health check-ups and blood tests can provide insights into how fasting is impacting your overall health.
Signs Indicating a Need for Changes
It’s important to recognize when your current fasting regimen may not be serving you as well as it could. Below is a table summarizing signs that indicate it may be time to adjust your fasting approach:
| Sign | Possible Adjustment |
|---|---|
| Persistent fatigue | Consider shortening fasting windows or adjusting meal quality. |
| Difficulty concentrating | Explore different fasting protocols or adjust fasting hours. |
| Increased irritability | Evaluate food choices during eating periods and hydration levels. |
| Weight plateau | Reassess calorie intake and incorporate exercise for better results. |
| Unmanageable hunger | Experiment with meal timing and composition, focusing on macronutrient balance. |
Keeping track of your intermittent fasting journey and making adjustments as needed can greatly improve your experience and results. By being proactive about monitoring your progress, you ensure that your approach is tailored to your individual needs and lifestyle.
Final Review
In summary, the Intermittent fasting guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to integrate fasting into your daily routine for improved health and vitality. By understanding the various methods and their benefits, you can choose a path that aligns with your personal goals and lifestyle. Remember, the journey to better health is about finding balance and making informed choices, and intermittent fasting may just be the key you’ve been looking for.
Common Queries
Can I drink coffee during fasting periods?
Yes, black coffee is typically allowed during fasting as it contains no calories and can even help suppress appetite.
Will intermittent fasting affect my workout performance?
Many find that intermittent fasting does not hinder their performance, but it might take some time to adjust. It’s essential to listen to your body and adapt your workout schedule accordingly.
Is intermittent fasting safe for everyone?
While intermittent fasting is safe for many, individuals with certain health conditions, such as diabetes or eating disorders, should consult a healthcare professional before starting.
Can I eat whatever I want during eating windows?
While it’s tempting to indulge, focusing on nutritious foods during eating periods can enhance the benefits of intermittent fasting.
How long does it take to see results from intermittent fasting?
Results can vary, but many people notice changes in their body and energy levels within a few weeks of consistent practice.